본 포스팅은 다음 포스팅으로 이어집니다 : keras를 이용한 mnist 숫자 데이터 분류(2)
데이터 전처리(preprocessing)
스케일링
- Normalization(MinMax)
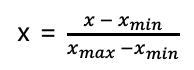
- Robust Normalization
사분위값을 이용한다. 이상치의 영향을 덜 받는다.
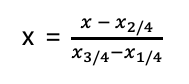
- Standardization
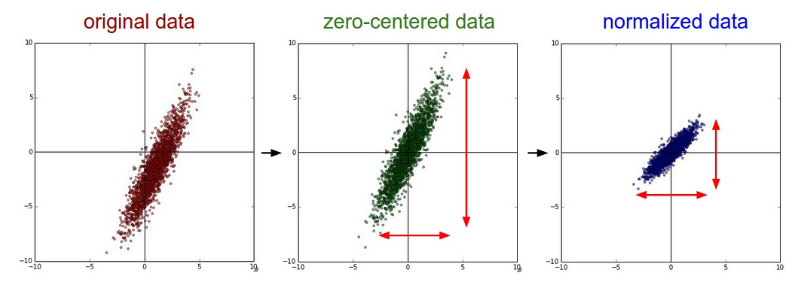
mean 차감을 통해 zero-centered화를 시켜주고 std로 나누어줌으로써 데이터가 일정 범위 안에 머무르게 한다.
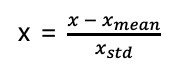
(x_train, y_train), (x_test, y_test) = load_data(path='mnist.npz')
# 60,000개 10000개
# 학습 데이터
print(x_train.shape, y_train.shape) # (60000, 28, 28) (60000,)
print(y_train) # [5 0 4 ... 5 6 8]
# 테스트 데이터
print(x_test.shape, y_test.shape) # (10000, 28, 28) (10000,)
print(y_test) # [7 2 1 ... 4 5 6]
np.random.seed(777)
sample_size = 3
# 0~59999에서 무작위 데이터 추출
random_idx = np.random.randint(60000, size=sample_size)
for idx in random_idx:
img = x_train[idx, :]
label = y_train[idx]
plt.figure()
plt.title('%d-th data, label is %d' % (idx, label))
plt.imshow(img)
# plt.show()
x_train, x_val, y_train, y_val = train_test_split(x_train, y_train,
test_size=0.3,
random_state=777)
# sklearn의 train_test_split 패키지를 이용해서 훈련데이터와 검증데이터로 7:3으로 나눔
# random-state는 seed와 동일. 데이터셋 추출을 랜덤으로 하기 때문.
print(f'훈련 데이터 {x_train.shape} 레이블 {y_train.shape}')
print(f'검증 데이터 {x_val.shape} 레이블 {y_val.shape}')
num_x_train = x_train.shape[0] # 42000
num_x_val = x_val.shape[0] # 18000
num_x_test = x_test.shape[0] # 10000
# print("num_x_train : ", num_x_train)
# print("num_x_val : ", num_x_val)
# print("num_x_test : ", num_x_test)
# 모델의 입력으로 사용하기 위한 전처리 과정입니다.
x_train = (x_train.reshape((num_x_train), 28*28)) / 255 # 훈련 데이터
x_val = (x_val.reshape((num_x_train), 28*28)) / 255 # 검증 데이터
x_test = (x_test.reshape((num_x_train), 28*28)) / 255 # 테스트 데이터
# Dense층에 데이터를 입력하기 위해 1차원 배열로 변환하는 것.
# 픽셀 값이 0~255의 범위에 있기 때문에 255로 나누어 줌. ( 각 입력 값을 0 ~ 1 로 표준화 해주었다는 의미 )
# 여기선 간단하게 255로 나누어졌지만, Minmax Normalization, Robust Normalization, Standardication 등의 방법이 주로 이용된다.
# 각 데이터 레이블을 범주형 형태로(one-hot-encoding) 변경한다.
y_train = to_categorical(y_train)
y_val = to_categorical(y_val)
y_test = to_categorical(y_test)모델 구성하기
Sequential 모델은 레이어를 선형으로 연결하여 구성합니다. 레이어 인스턴스를 생성자에게 넘겨줌으로써 Sequential 모델을 구성할 수 있습니다.
from keras.models import Sequential
from keras.layers import Dense, Activation
model = Sequential([
Dense(32, input_shape=(784,)),
Activation('relu'),
Dense(10),
Activation('softmax'),
])또한, .add() 메소드를 통해서 쉽게 레이어를 추가할 수 있습니다
model = Sequential()
model.add(Dense(32, input_dim=784))
model.add(Activation('relu'))- 모델 구성하기
model = Sequential()- Node 구성하기
# input layer 형태를 반드시 명시해야함.
# 784 -> 64인 첫번째 Dense층
model.add(Dense(64, activation='relu', input_shape=(784,))) # 입력 층
model.add(Dense(32, activation='relu')) # 32개의 출력을 가지는 Dense층 # hidden layer
model.add(Dense(10, activation='softmax')) # 10개의 출력을 가지는 출력망. 출력Node이므로 'softmax'를 사용한다. # 출력 층- 학습과정 설정하기
- 마지막 단계에서
손실함수,옵티마이저,평가지표를 설정한다.
# 학습과정 설정하기
model.compile(optimizer='adam',
loss='categorical_crossentropy',
# 모니터링할 평가 지표
metrics=['acc']
) # adam optimizer의 기본 학습률은 0.001로 고정되어 있음.- 손실함수는 예측값과 레이블간의 차이에 대한 값을 계산하는 함수이다. 일반적인 경우 손실함수의 미분함수에 예측값과 레이블값을 집어넣어 출력된 값을 이용하여, optimizer 의 방법론에 따라 가중값W를 수정하게 된다.
- 손실함수를 통해 계산된 손실값은
history.history['loss']에 저장된다.
- 모델 학습하기
# 모델 학습 명령.
history = model.fit(x_train, y_train,
epochs=30,
batch_size=128,
validation_data=(x_val, y_val))
# 1 epoch는 훈련 데이터 42000/128 = 328.125회의 훈련을 시행하여 전체 데이터를 소진한 것이 1epoch이다.
# 따라서 본 모델은 총 9843.75번의 batch 훈련을 하게 된다.- history를 통해 확인할 수 있는 값 출력하기
print(history.history.keys())
# dict_keys(['loss', 'acc', 'val_loss', 'val_acc'])- 학습결과 그려보기
# history를 통해 확인할 수 있는 값 출력하기
print(history.history.keys())
his_dict = history.history
loss = his_dict['loss']
val_loss = his_dict['val_loss'] # 검증데이터에 적용한 loss
epochs = range(1, len(loss) + 1)
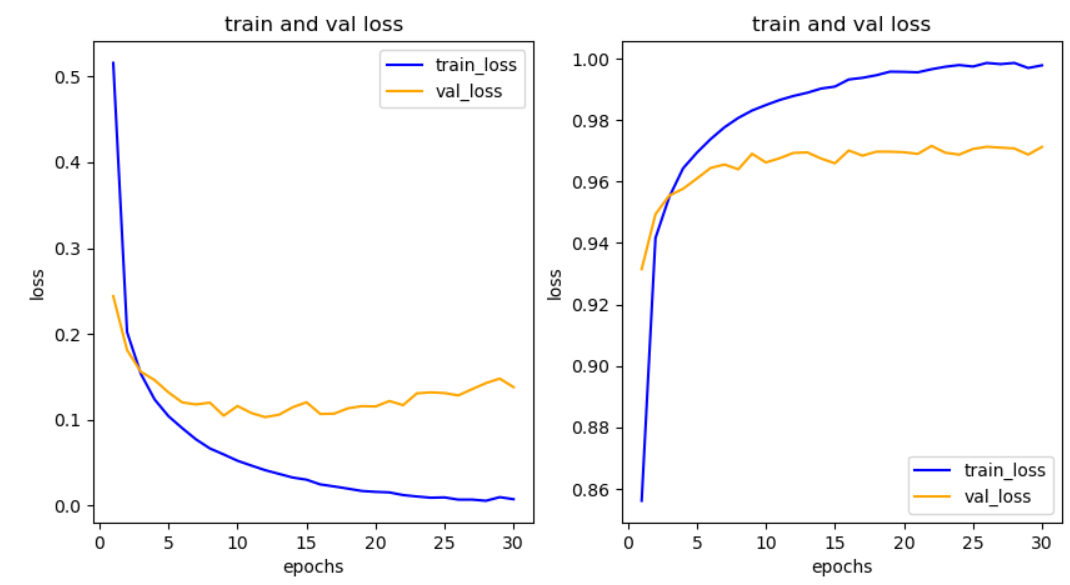
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(10, 5))# 훈련 및 검증 손실 그리기
ax1 = fig.add_subplot(1, 2, 1)
ax1.plot(epochs, loss, color='blue', label='train_loss')
ax1.plot(epochs, val_loss, color='orange', label='val_loss')
ax1.set_title('train and val loss')
ax1.set_xlabel('epochs')
ax1.set_ylabel('loss')
ax1.legend()
acc = his_dict['acc']
val_acc = his_dict['val_acc']
# 훈련 및 검증 정확도 그리기
ax2 = fig.add_subplot(1, 2, 2)
ax2.plot(epochs, acc, color='blue', label='train_loss')
ax2.plot(epochs, val_acc, color='orange', label='val_loss')
ax2.set_title('train and val loss')
ax2.set_xlabel('epochs')
ax2.set_ylabel('loss')
ax2.legend()
plt.show()figure.add_subplot: Add an Axes to the figure as part of a subplot arrangement.- Either a 3-digit integer or three separate integers describing the position of the subplot. If the three integers are nrows, ncols, and index in order, the subplot will take the index position on a grid with nrows rows and ncols columns. index starts at 1 in the upper left corner and increases to the right.
add_subplot(nrows, ncols, index, **kwargs)- 1행 2열의 테이블을 만들고, 1번째 자리에
훈련 및 검증 손실 그래프를 그린다. 2번째 자리에훈련 및 검증 정확도 그래프를 그린다.
'Python > Python 딥러닝' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Keras를 이용한 보스턴 주택가격 예측 + K-Fold (0) | 2020.07.15 |
|---|---|
| keras를 이용한 mnist 숫자 데이터 분류(2) (0) | 2020.07.13 |
| Keras에서 개발 과정, 활성화함수, 옵티마이저, 손실함수, 평가지표란? (0) | 2020.07.13 |
| 파이썬_확률적 경사 하강법-SGD(Stochastic Gradient Descent) (1) | 2020.07.13 |
| [tensorflow]텐서 선언하기, 즉시 실행모드를 통한 연산, @tf.function (0) | 2020.07.10 |
본 포스팅은 다음 포스팅으로 이어집니다 : keras를 이용한 mnist 숫자 데이터 분류(2)
데이터 전처리(preprocessing)
스케일링
- Normalization(MinMax)
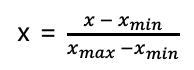
- Robust Normalization
사분위값을 이용한다. 이상치의 영향을 덜 받는다.
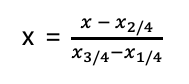
- Standardization
mean 차감을 통해 zero-centered화를 시켜주고 std로 나누어줌으로써 데이터가 일정 범위 안에 머무르게 한다.
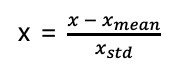

(x_train, y_train), (x_test, y_test) = load_data(path='mnist.npz')
# 60,000개 10000개
# 학습 데이터
print(x_train.shape, y_train.shape) # (60000, 28, 28) (60000,)
print(y_train) # [5 0 4 ... 5 6 8]
# 테스트 데이터
print(x_test.shape, y_test.shape) # (10000, 28, 28) (10000,)
print(y_test) # [7 2 1 ... 4 5 6]
np.random.seed(777)
sample_size = 3
# 0~59999에서 무작위 데이터 추출
random_idx = np.random.randint(60000, size=sample_size)
for idx in random_idx:
img = x_train[idx, :]
label = y_train[idx]
plt.figure()
plt.title('%d-th data, label is %d' % (idx, label))
plt.imshow(img)
# plt.show()
x_train, x_val, y_train, y_val = train_test_split(x_train, y_train,
test_size=0.3,
random_state=777)
# sklearn의 train_test_split 패키지를 이용해서 훈련데이터와 검증데이터로 7:3으로 나눔
# random-state는 seed와 동일. 데이터셋 추출을 랜덤으로 하기 때문.
print(f'훈련 데이터 {x_train.shape} 레이블 {y_train.shape}')
print(f'검증 데이터 {x_val.shape} 레이블 {y_val.shape}')
num_x_train = x_train.shape[0] # 42000
num_x_val = x_val.shape[0] # 18000
num_x_test = x_test.shape[0] # 10000
# print("num_x_train : ", num_x_train)
# print("num_x_val : ", num_x_val)
# print("num_x_test : ", num_x_test)
# 모델의 입력으로 사용하기 위한 전처리 과정입니다.
x_train = (x_train.reshape((num_x_train), 28*28)) / 255 # 훈련 데이터
x_val = (x_val.reshape((num_x_train), 28*28)) / 255 # 검증 데이터
x_test = (x_test.reshape((num_x_train), 28*28)) / 255 # 테스트 데이터
# Dense층에 데이터를 입력하기 위해 1차원 배열로 변환하는 것.
# 픽셀 값이 0~255의 범위에 있기 때문에 255로 나누어 줌. ( 각 입력 값을 0 ~ 1 로 표준화 해주었다는 의미 )
# 여기선 간단하게 255로 나누어졌지만, Minmax Normalization, Robust Normalization, Standardication 등의 방법이 주로 이용된다.
# 각 데이터 레이블을 범주형 형태로(one-hot-encoding) 변경한다.
y_train = to_categorical(y_train)
y_val = to_categorical(y_val)
y_test = to_categorical(y_test)모델 구성하기
Sequential 모델은 레이어를 선형으로 연결하여 구성합니다. 레이어 인스턴스를 생성자에게 넘겨줌으로써 Sequential 모델을 구성할 수 있습니다.
from keras.models import Sequential
from keras.layers import Dense, Activation
model = Sequential([
Dense(32, input_shape=(784,)),
Activation('relu'),
Dense(10),
Activation('softmax'),
])또한, .add() 메소드를 통해서 쉽게 레이어를 추가할 수 있습니다
model = Sequential()
model.add(Dense(32, input_dim=784))
model.add(Activation('relu'))- 모델 구성하기
model = Sequential()- Node 구성하기
# input layer 형태를 반드시 명시해야함.
# 784 -> 64인 첫번째 Dense층
model.add(Dense(64, activation='relu', input_shape=(784,))) # 입력 층
model.add(Dense(32, activation='relu')) # 32개의 출력을 가지는 Dense층 # hidden layer
model.add(Dense(10, activation='softmax')) # 10개의 출력을 가지는 출력망. 출력Node이므로 'softmax'를 사용한다. # 출력 층- 학습과정 설정하기
- 마지막 단계에서
손실함수,옵티마이저,평가지표를 설정한다.
# 학습과정 설정하기
model.compile(optimizer='adam',
loss='categorical_crossentropy',
# 모니터링할 평가 지표
metrics=['acc']
) # adam optimizer의 기본 학습률은 0.001로 고정되어 있음.- 손실함수는 예측값과 레이블간의 차이에 대한 값을 계산하는 함수이다. 일반적인 경우 손실함수의 미분함수에 예측값과 레이블값을 집어넣어 출력된 값을 이용하여, optimizer 의 방법론에 따라 가중값W를 수정하게 된다.
- 손실함수를 통해 계산된 손실값은
history.history['loss']에 저장된다.
- 모델 학습하기
# 모델 학습 명령.
history = model.fit(x_train, y_train,
epochs=30,
batch_size=128,
validation_data=(x_val, y_val))
# 1 epoch는 훈련 데이터 42000/128 = 328.125회의 훈련을 시행하여 전체 데이터를 소진한 것이 1epoch이다.
# 따라서 본 모델은 총 9843.75번의 batch 훈련을 하게 된다.- history를 통해 확인할 수 있는 값 출력하기
print(history.history.keys())
# dict_keys(['loss', 'acc', 'val_loss', 'val_acc'])- 학습결과 그려보기
# history를 통해 확인할 수 있는 값 출력하기
print(history.history.keys())
his_dict = history.history
loss = his_dict['loss']
val_loss = his_dict['val_loss'] # 검증데이터에 적용한 loss
epochs = range(1, len(loss) + 1)
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(10, 5))# 훈련 및 검증 손실 그리기
ax1 = fig.add_subplot(1, 2, 1)
ax1.plot(epochs, loss, color='blue', label='train_loss')
ax1.plot(epochs, val_loss, color='orange', label='val_loss')
ax1.set_title('train and val loss')
ax1.set_xlabel('epochs')
ax1.set_ylabel('loss')
ax1.legend()
acc = his_dict['acc']
val_acc = his_dict['val_acc']
# 훈련 및 검증 정확도 그리기
ax2 = fig.add_subplot(1, 2, 2)
ax2.plot(epochs, acc, color='blue', label='train_loss')
ax2.plot(epochs, val_acc, color='orange', label='val_loss')
ax2.set_title('train and val loss')
ax2.set_xlabel('epochs')
ax2.set_ylabel('loss')
ax2.legend()
plt.show()figure.add_subplot: Add an Axes to the figure as part of a subplot arrangement.- Either a 3-digit integer or three separate integers describing the position of the subplot. If the three integers are nrows, ncols, and index in order, the subplot will take the index position on a grid with nrows rows and ncols columns. index starts at 1 in the upper left corner and increases to the right.
add_subplot(nrows, ncols, index, **kwargs)- 1행 2열의 테이블을 만들고, 1번째 자리에
훈련 및 검증 손실 그래프를 그린다. 2번째 자리에훈련 및 검증 정확도 그래프를 그린다.

'Python > Python 딥러닝' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Keras를 이용한 보스턴 주택가격 예측 + K-Fold (0) | 2020.07.15 |
|---|---|
| keras를 이용한 mnist 숫자 데이터 분류(2) (0) | 2020.07.13 |
| Keras에서 개발 과정, 활성화함수, 옵티마이저, 손실함수, 평가지표란? (0) | 2020.07.13 |
| 파이썬_확률적 경사 하강법-SGD(Stochastic Gradient Descent) (1) | 2020.07.13 |
| [tensorflow]텐서 선언하기, 즉시 실행모드를 통한 연산, @tf.function (0) | 2020.07.10 |
